문제
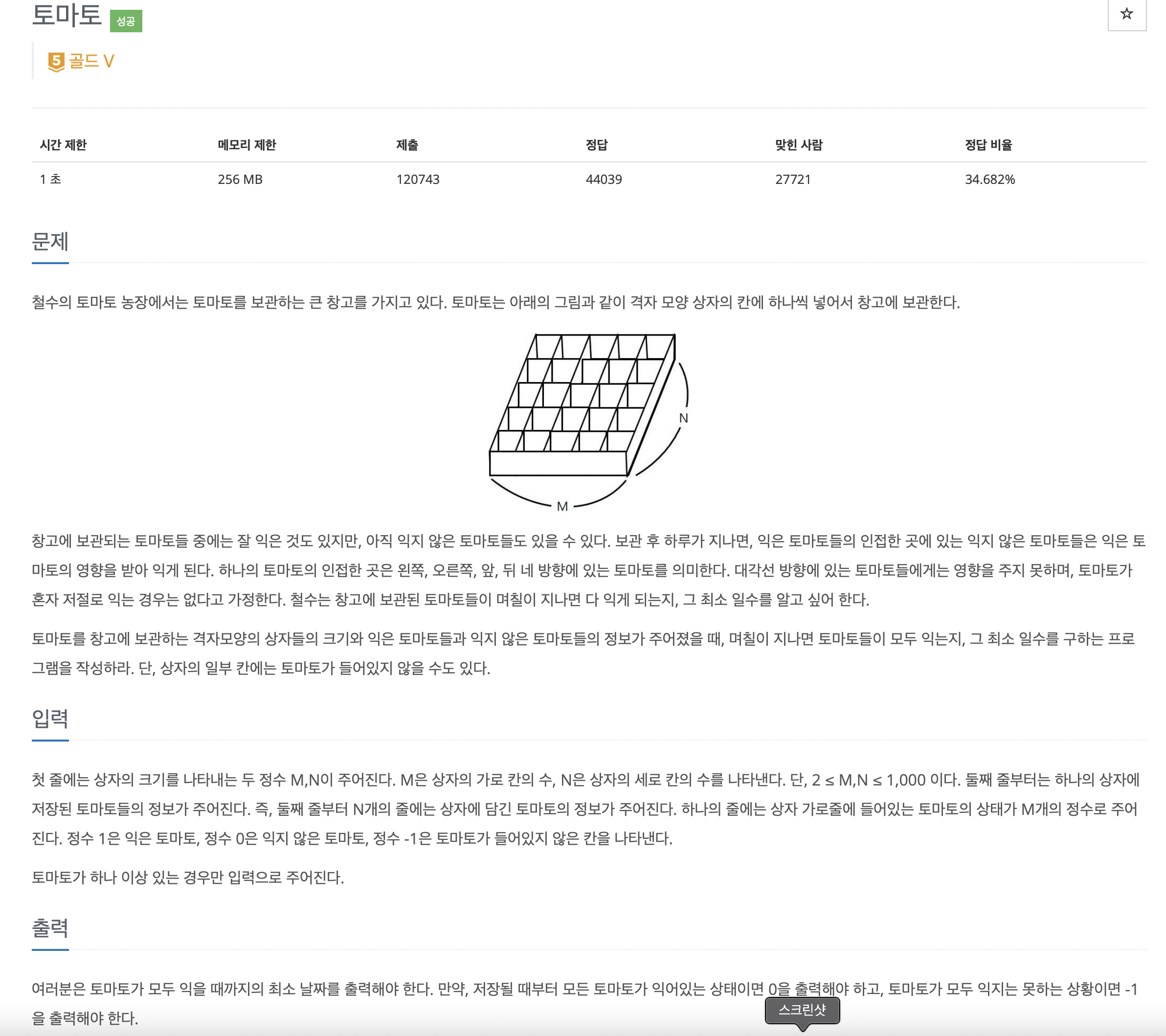
아이디어: BFS
진짜 전형적인 BFS 응용 문제이다.
토마토가 익는 시간을 함께 queue에 넣어서 저장한 다음, 익는 시간이 특정 시간을 지나고 나면 하루가 지난 것으로 판별해야 한다.
또한 맨 처음에 queue에 넣는 좌표는 토마토가 있는 좌표를 모두 넣는다. 이때 시간대는 모두 0으로 초기화 한다.
토마토가 이동할 수 있는 동서남북 4 방향에 대해서 토마토가 없는 경우에 값을 바꾸고 queue에 넣어준다. 이때는 (이전시간 + 1)로 설정하여서 넣어준다.
구현
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int dx[4] = {0, 0, 1, -1};
int dy[4] = {1, -1, 0, 0};
int m, n;
int graph[1001][1001];
vector<pair<int, int>> tomato;
int BFS()
{
int result = -1;
// {{좌표 x, 좌표 y}, 시간} -> 이래야 하루를 계산 할 수 있음
queue<pair<pair<int, int>, int>> pq;
// 토마토가 익어있는 곳을 출발지점으로 설정
for(auto iter : tomato)
pq.push({{iter.first, iter.second}, 0});
int prev = -1;
while(!pq.empty())
{
int x = pq.front().first.first;
int y = pq.front().first.second;
int time = pq.front().second;
// 현재 토마토의 시간이 이전시간과 다른 경우, 즉 하루가 지난 경우 result++ 하고 값 바꿔줌
if (prev != time)
{
prev = time;
result++;
}
pq.pop();
// 토마토의 진행 방향 동서남북 4가지에 대하여 확인
for(int dir = 0;dir < 4;dir++)
{
int tempX = x + dx[dir];
int tempY = y + dy[dir];
// 바운더리 체크
if (tempX < 0 || tempY < 0 || tempX >= n || tempY >= m)
continue;
// 토마토가 안 익은 경우에 토마토를 익는 것으로 바꿈
if (graph[tempX][tempY] == 0)
{
graph[tempX][tempY] = 1;
// 시간을 넣을 때에는 (이전시간 + 1)을 해서 하루가 지났음을 체크
pq.push({{tempX, tempY}, time + 1});
}
}
}
return result;
}
int main()
{
// m(가로), n(세로)
cin>>m>>n;
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++)
{
for(int j = 0;j < m;j++)
{
cin>>graph[i][j];
// 익은 토마토의 좌표를 따로 저장
if (graph[i][j] == 1)
tomato.push_back({i, j});
}
}
int result = BFS();
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++)
{
for(int j = 0;j < m;j++)
{
// 토마토가 익지 못하는 경우
if (graph[i][j] == 0)
{
cout<<-1<<endl;
return 0;
}
}
}
cout<<result<<endl;
return 0;
}'ALGORITHM > c&c++ baekjoon' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [C++/1697, 11779] 탐색 중 이전 값를 저장해야 하는 유형의 문제들 (0) | 2022.05.17 |
|---|---|
| [C++/3665] 최종 순위 - using 위상 정렬 (topology sort) (0) | 2022.05.14 |
| [C++/2887] 행성 터널 - using MST : Kruskal Algorithm (0) | 2022.05.11 |
| [C++/16234] 인구 이동 - using BFS (0) | 2022.05.06 |
| [C++/3190] 뱀 - Implementation (0) | 2022.05.06 |